Two planes of charge with no thickness, A and B, are parallel and vertical. The electric field in region I to the left of plane A has magnitude 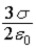 and points to the left. The electric field in the region to the right of B has magnitude
and points to the left. The electric field in the region to the right of B has magnitude 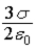 and points to the right. The electric field in the region between the two planes has magnitude
and points to the right. The electric field in the region between the two planes has magnitude 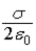 and points to the right. The surface charge density on planes A and B, respectively, is
and points to the right. The surface charge density on planes A and B, respectively, is
Definitions:
Inventory Levels
The quantity of goods and materials a company has in stock at a given time, crucial for meeting customer demand and planning production.
Contribution Margin Ratio
A financial metric that indicates the portion of sales revenue that exceeds variable costs and contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Fixed Costs
Costs that remain constant regardless of the amount of goods produced or sold, including expenses like rent, wages, and insurance.
Unit Variable Cost
The cost that varies directly with the production volume, defined per unit of production.
Q3: A rectangle has a length of 1.323
Q6: Find the pressure in atmospheres in the
Q8: A 30-μF capacitor is charged to 40
Q14: Most telephone cables are made of copper
Q18: If a = 60 cm, b =
Q19: A company that produces pulsed gas heaters
Q37: Two harmonic waves traveling in opposite directions
Q43: Which of the graphs below shows a
Q78: Charge of uniform density (40 pC/m<sup>2</sup>) is
Q79: Which one of the following is not