The forces that determine the size of groups (“swarms”) of social insects and the rates at which they grow are not well understood. Biologists have observed large variability in the size of swarms across species. In a study of the social wasp, Polybia occidentalis, investigators dismantled a nest of these insects and marked a few insects for future identification in new swarms. Twenty-five days after dismantling the original swarm they had located new swarms of wasps from the original colonies.
-Using your box plots 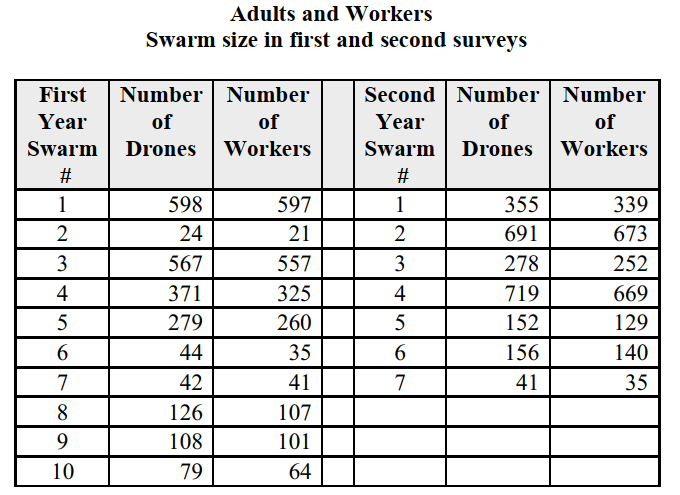 , compare the distributions of first and second yeardrones. Justify your comparisons by appealing to specific aspects of the box plotsconstructed in
, compare the distributions of first and second yeardrones. Justify your comparisons by appealing to specific aspects of the box plotsconstructed in 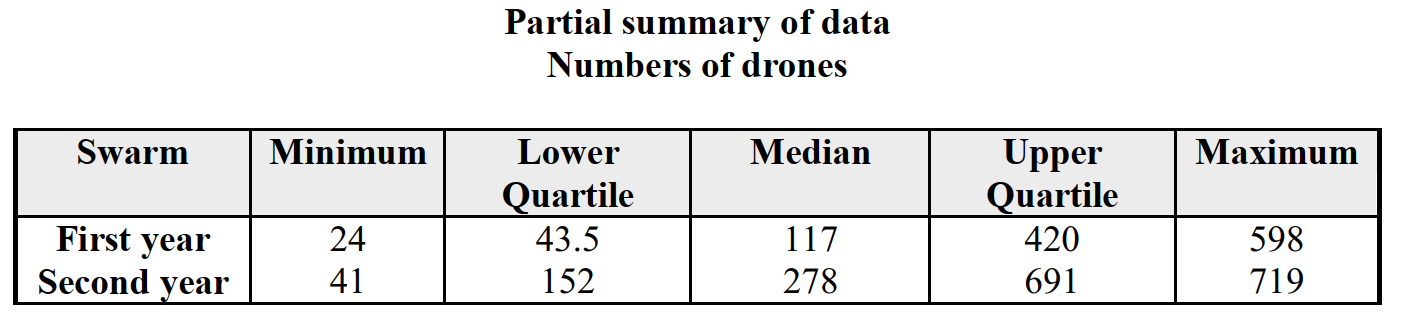
Definitions:
Direct Materials
The specific raw materials used in the production of goods that can be directly attributed to the finished product, contributing directly to its manufacture.
Factory Depreciation
The decrease in value of manufacturing facilities and equipment over time due to wear and tear or obsolescence.
Cost of Goods Manufactured
The total expense incurred by a company to produce goods during a specific period, including labor, material, and overhead costs.
Manufacturing Overhead
All manufacturing costs excluding direct materials and direct labor.
Q8: A plane lamina with constant density
Q14: In a study of texting and
Q26: The width of the confidence interval for
Q30: A report in the Des Moines
Q35: A simple random sample of 10
Q37: Bias is a potentially serious problem that
Q56: Let <span class="ql-formula" data-value="S"><span class="katex"><span
Q82: One of the major objectives of the
Q116: The World Bank operates primarily as a<br>A)
Q119: Which of the following describes the vicious