Definitions:
Breach of Contract
The violation of any of the agreed-upon terms and conditions in a binding contract.
Punitive Damages
Financial compensation awarded to a plaintiff, beyond actual damages, to punish the defendant for egregious conduct.
Breaches Contract
A violation or infringement of the terms and conditions stated in a contract by any of the parties involved, leading to a breach of contract.
Profit on Resale
The financial gain obtained from selling an asset for more than its purchase price.
Q45: The transactions demand for money will decrease
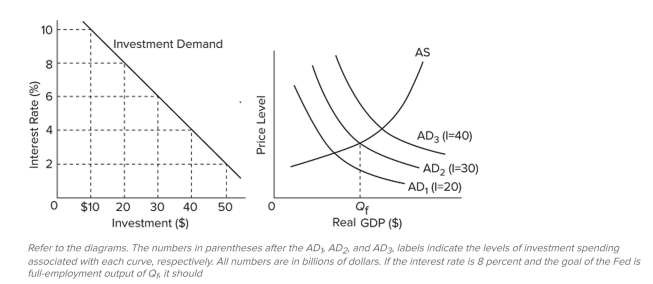
Q68: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8601/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q70: The reserves of a commercial bank consist
Q155: When a company declares bankruptcy, stockholders are
Q165: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array} { | c |
Q179: Assume the legal reserve ratio is 25
Q211: A commercial bank can expand its excess
Q263: A 10 percent rate of interest will
Q281: After the 2008 financial crisis, why did
Q284: A commercial bank has excess reserves of