Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 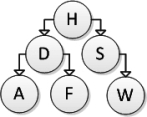 Consider the following addNode method for inserting a newNode into a binary search tree:
Consider the following addNode method for inserting a newNode into a binary search tree:
public void addNode(Node newNode)
{
int comp = newnode.data.compareTo(data) ;
if (comp < 0)
{
if (left == null) {left = newNode;}
else { left.addNode(newNode) ; }
}
else
{
if (right == null) {right = newNode;}
else { right.addNode(newNode) ; }
}
}
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element B, calling addNode on the root of the tree? 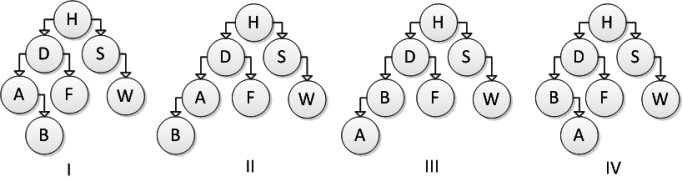
Definitions:
Q5: Which statement stores an integer value in
Q21: _ is often described as the has-a
Q27: The term "stale data" refers to a
Q29: Which of the following statements about the
Q32: What do object variables store?<br>A)objects<br>B)classes<br>C)object references<br>D)numbers
Q32: What code would be the most appropriate
Q64: Consider the following binary search tree diagram:
Q65: Assume that recursive method search returns true
Q66: Selection sort has O(n<sup>2</sup>) complexity.If a computer
Q70: One way to handle collisions in a