Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 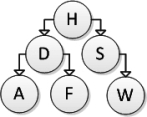 Consider the following addNode method for inserting a newNode into a binary search tree:
Consider the following addNode method for inserting a newNode into a binary search tree:
public void addNode(Node newNode)
{
int comp = newnode.data.compareTo(data) ;
if (comp < 0)
{
if (left == null) {left = newNode;}
else { left.addNode(newNode) ; }
}
else
{
if (right == null) {right = newNode;}
else { right.addNode(newNode) ; }
}
}
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element T, calling addNode on the root of the tree? 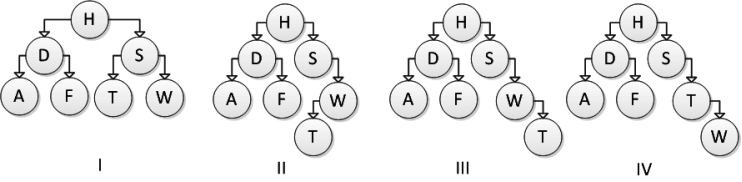
Definitions:
Annual Interest Rate
The percentage rate charged or paid over a period of one year for a loan or investment.
Compounds Interest Continuously
The process of calculating interest on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods, assumed to be compounded infinitely often per period.
Nearest Tenth
Rounding a number to one decimal place, or to the closest tenth.
Compounded Continuously
Refers to the mathematical limit of the compound interest formula, as the number of compounding periods per year becomes infinitely large.
Q12: Which of the following represents a method
Q24: Given the following code snippet: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7392/.jpg"
Q29: Which statement about handling collisions in a
Q40: Consider the following recursive code snippet: <img
Q50: What is the name of the type
Q54: Which class is used for output of
Q64: If the method makeMenuItem is called four
Q66: A termination condition in a loop is
Q73: Which method of the Stream class can
Q74: Which of the following represents a method