Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
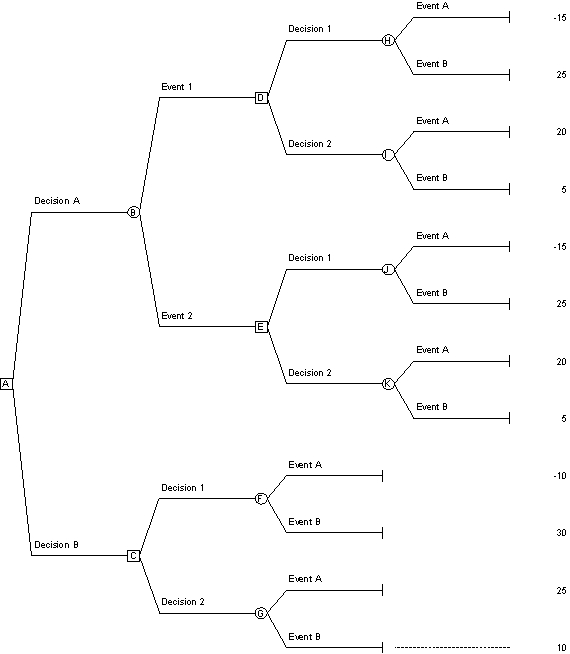
-A decision tree is:
Definitions:
Test Statistic
An outcome obtained from samples in a hypothesis experiment, crucial in deciding if the null hypothesis should be dismissed.
P-value
Assuming the correctness of the null hypothesis, it is the possibility of obtaining test results that are equally or more extreme than those observed.
Sample Standard Deviation
A measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values in a sample.
Null Hypothesis
A default hypothesis that there is no statistical significance in a set of given observations, aiming to be either rejected or not rejected based on test results.
Q3: Some demographic characteristics are more important than
Q3: Distinguish among the jobs of producers', wholesalers',
Q9: What does it mean to say that
Q10: Firms producing differentiated products face downward-sloping demand.
Q14: A Cournot oligopoly has 2 firms,
Q18: Discuss a few changes in the market
Q40: The domestic market for calculators is
Q45: A monopolist faces two consumer groups:
Q52: To be efficient, a competitive equilibrium must
Q69: For a perfectly competitive firm,