Phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide or amino acid sequences can be constructed using various algorithms. One simple algorithm is based on a matrix of pairwise genetic distances (divergences) calculated after multiple alignment of the sequences. Imagine you have aligned a particular gene from different hominids (humans and the great apes), and have estimated the normalized number of nucleotide substitutions that have occurred in this gene in each pair of organisms since their divergence from their last common ancestor. You have obtained the following distance matrix.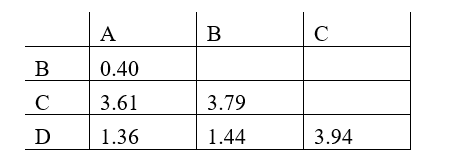
Answer the following question(s) based on this matrix.
-If species A in the distance matrix represents human, indicate which of the other species (B to D) represents chimpanzee, gorilla, and orangutan, respectively. Your answer would be a three-letter string composed of letters B, C, and D only, e.g. DCB.
Definitions:
Lateralization
The tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be more dominant in one hemisphere of the brain than the other.
Amygdala
A region of the brain involved in experiencing emotions, such as fear and pleasure.
Motor Cortex
A region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
Frontal Lobes
Regions of the brain located at the front part of the cerebral cortex, involved in decision making, problem-solving, control of purposeful behaviors, consciousness, and emotions.
Q3: Sort the following from a low to
Q7: African American churches in the U.S.have played
Q7: Indicate whether each of the following is
Q20: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q27: Most fish genomes are at least 1
Q29: Explain the social and the psychological functions
Q33: A hydrophobic molecule is typically …<br>A) able
Q44: In assembling a nucleosome, normally the …(1)
Q45: This large and complex general transcription factor
Q77: The revenue generated by Wal-Mart is equivalent