Solve the problem.
-The average weight of a particular species of frog is given 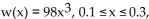 where x is length (with legs stretched out) in meters and w(x) is weight in grams. (i) Describe how the graph of function w can be
where x is length (with legs stretched out) in meters and w(x) is weight in grams. (i) Describe how the graph of function w can be
Obtained from one of the six basic functions: 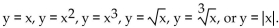 . (ii) Sketch a graph of
. (ii) Sketch a graph of
Function w using part (i) as an aid. 
Definitions:
Plasticity
The capacity of the brain to change and adapt in response to experience, learning, or injury.
Brain
The complex organ located in the skull of vertebrates that is the center of the nervous system, responsible for controlling thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger, and every process that regulates our body.
Adapt
To make suitable adjustments to new conditions or environments.
Action Potential
A temporary reversal of an electrical charge across a cell membrane resulting in the transmission of a nerve impulse.
Q10: The Old-World Class Ring Company designs and
Q13: For which of the following types of
Q14: Suppose an horse feed to be mixed
Q25: Assume your current projects will return $560
Q25: The Southern States Ring Company designs and
Q30: You can invest in a fully taxable
Q36: Change to simplest radical form: m: <img
Q44: Assume you live (or invest)in a country
Q50: Justin invested $5,000 in Stock A. Although
Q80: {all odd integers greater than -3 and