Using the z-table (Table E) , find the critical value (or values) for an 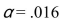 left-tailed test.
left-tailed test.
Definitions:
Type I Error
A Type I Error occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, often referred to as a "false positive."
Type II Error
A statistical error made when failing to reject a false null hypothesis, also known as a false negative.
Null Hypothesis
is a default hypothesis that there is no significant difference or effect.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis proposes that there is a statistically significant difference between data sets or effects, contrary to the null hypothesis.
Q8: In a(n) _, the null hypothesis should
Q14: A garbage collector believes that he averages
Q15: A researcher is comparing three groups of
Q25: A product testing laboratory selected a sample
Q30: In a sample of 50 mice, a
Q33: A lumber mill is tested for consistency
Q36: Two independent sets of data are collected,
Q37: The median can be a more appropriate
Q40: Two students were asked to rate six
Q62: Which of the following examples of a