Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required.If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it.If the problem seems to
Require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution.
A cyclist is riding on a path whose elevation is modeled by the function  where x and
where x and 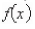 are measured in miles.Find the rate of change of elevation when x = 5.
are measured in miles.Find the rate of change of elevation when x = 5. 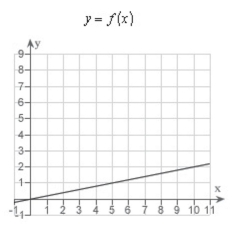
Definitions:
Symbolic Interactionism
A sociological perspective that emphasizes the role of symbols and language in the creation of social realities and individual identities.
Bidirectional Causal Relationship
A relationship where two variables influence each other, with each variable being both a cause and an effect in the relationship.
Conscientious Employees
Workers who are diligent, careful, and thorough in their job responsibilities and tasks.
Positive Affect
A dimension of emotional experience characterized by feelings of happiness, joy, and enthusiasm.
Q2: Use the differential equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8202/.jpg" alt="Use
Q4: The formula for the power output of
Q10: Suppose a planet is discovered that revolves
Q11: The maker of an automobile advertises that
Q16: Use left endpoints and 10 rectangles to
Q20: Suppose a ball is dropped from a
Q42: Find the polar equation for the curve
Q43: Write an equation of the line that
Q88: If a projectile is fired with an
Q94: Determine which series is convergent.