SCENARIO 15-4 The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing) , daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance) , mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries) , and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending) of 47 schools in the state. Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 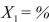 Attendance,
Attendance, 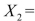 Salaries and
Salaries and 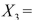 Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination (
Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination ( 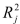 ) of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
) of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 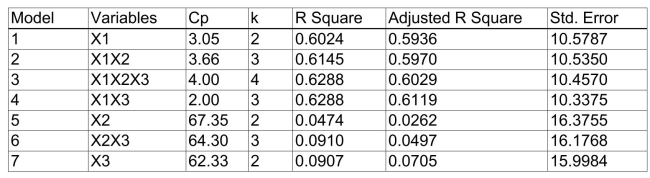 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 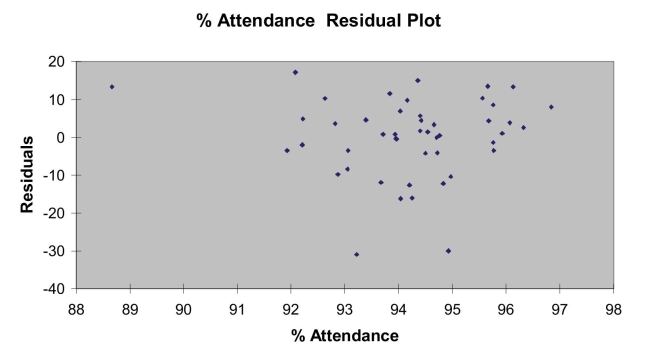 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models: 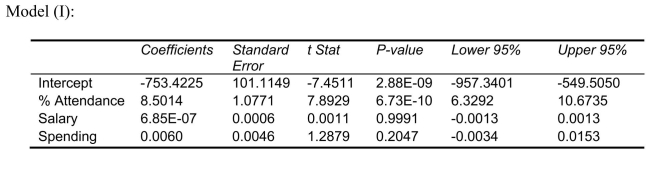
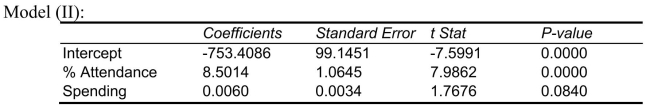
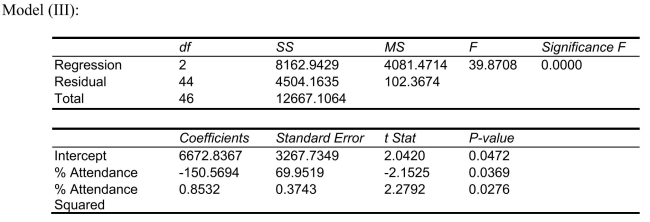
-Referring to Scenario 15-4, the "best" model using a 5% level of significance among those chosen by the 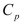 statistic is
statistic is
Definitions:
External Frustration
Emotional or psychological stress resulting from blockages or hindrances caused by environmental factors outside an individual's control.
Avoidance-Avoidance Conflict
A psychological dilemma wherein an individual must choose between two undesirable outcomes.
Unfinished Paper
A written document that is not completed, often lacking essential content, conclusions, or final editing.
Failing Grade
An academic assessment outcome indicating that the level of performance did not meet the minimum criteria for passing.
Q4: Referring to Scenario 16-12, the best interpretation
Q8: Referring to Scenario 14-4, which of the
Q42: The logarithm transformation can be used<br>A)to overcome
Q58: Referring to Scenario 17-4, what percentage of
Q63: Referring to Scenario 15-6, the variable x₁
Q66: Referring to Scenario 17-1, the sparklines enable
Q67: In a classification tree, the dependent variable
Q105: Referring to Scenario 16-13, what is the
Q117: Referring to Scenario 14-10, to test the
Q226: Referring to Scenario 14-15, what is the