SCENARIO 15-4 The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing) , daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance) , mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries) , and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending) of 47 schools in the state. Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 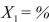 Attendance,
Attendance, 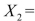 Salaries and
Salaries and 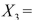 Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination (
Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination ( 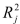 ) of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
) of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 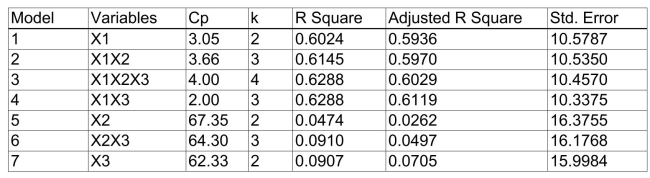 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 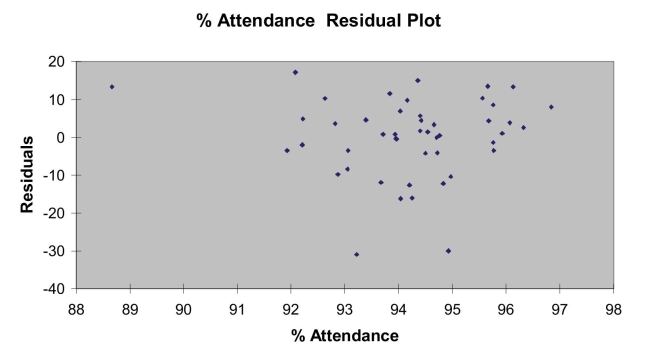 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models: 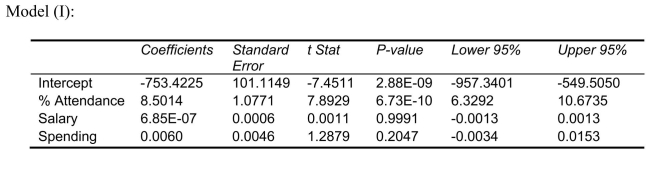
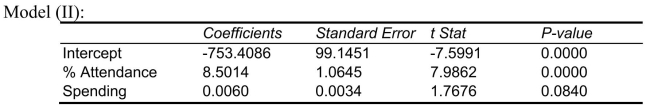
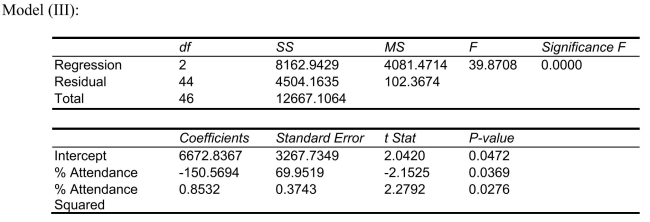
-Referring to Scenario 15-4, the better model using a 5% level of significance derived from the "best" model above is
Definitions:
Consumer Surplus
The benefit obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay.
Optimal Consumption
refers to the situation in which a consumer allocates their income in a way that maximizes their overall satisfaction or utility, given their preferences and the prices of goods and services.
Demand Schedule
A demand schedule is a table that shows the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
Price Elasticity
A measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
Q2: Each forecast using the method of exponential
Q22: Referring to Scenario 18-6, what is the
Q96: Neural networks use the validating data to
Q107: An insurance company evaluates many variables about
Q111: Referring to Scenario 16-5, exponentially smooth the
Q126: An airline wants to select a computer
Q198: A quality control manager at a plant
Q218: Referring to Scenario 14-19, there is not
Q229: A regression had the following results: SST
Q265: In a multiple regression problem involving two