SCENARIO 15-4 The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance), mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending)of 47 schools in the state. Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 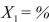 Attendance,
Attendance, 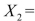 Salaries and
Salaries and 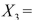 Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination (
Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination ( 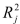 )of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
)of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 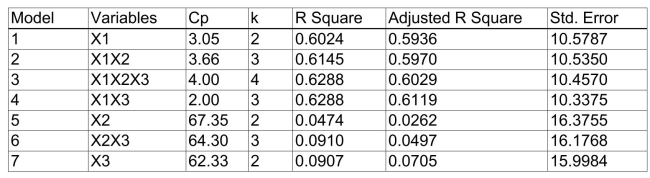 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 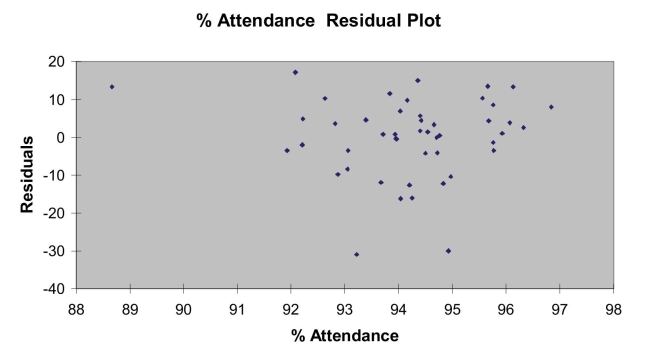 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
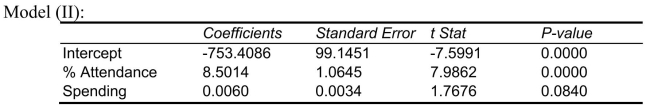
Following is the output of several multiple regression models: 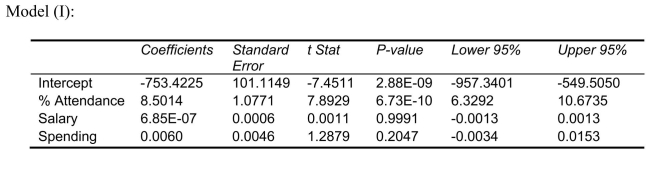
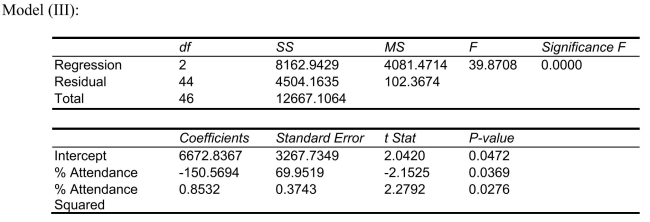
-Referring to Scenario 15-4, the quadratic effect of daily average of the percentage of students attending class on percentage of students passing the proficiency test is not significant at a 5% level of significance.
Definitions:
Smoking Cessation Classes
Educational programs designed to provide individuals with strategies and support to quit smoking.
Health Awareness Programs
Initiatives designed to inform and educate individuals or communities about important health issues, promoting healthier lifestyles and preventive health practices.
Preventable Illnesses
Diseases that can be avoided through preventive measures, such as vaccinations or healthy lifestyle choices.
Chronic Diseases
Long-lasting medical conditions that are persistent and typically require long-term management or care.
Q26: Referring to Scenario 17-1, the pattern of
Q37: Referring to Scenario 16-9 and using a
Q40: Referring to Scenario 18-8, the null hypothesis
Q47: Referring to Scenario 15-4, the "best" model
Q57: Referring to Scenario 16-12, using the regression
Q57: Referring to Scenario 15-6, the model that
Q61: Referring to Scenario 18-8, what are the
Q91: The stepwise regression approach takes into consideration
Q168: Referring to Scenario 16-13, the best model
Q326: Referring to Scenario 14-8, the analyst decided