SCENARIO 18-4 You decide to predict gasoline prices in different cities and towns in the United States for your term project.Your dependent variable is price of gasoline per gallon and your explanatory variables are per capita income, the number of firms that manufacture automobile parts in and around the city, the number of new business starts in the last year, population density of the city, percentage of local taxes on gasoline, and the number of people using public transportation.You collected data of 32 cities and obtained a regression sum of squares SSR= 122.8821.Your computed value of standard error of the estimate is 1.9549.
-Referring to Scenario 18-4, the value of adjusted 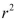 is
is
Definitions:
Barriers to Entry
Barriers to entry are obstacles that make it difficult for new competitors to enter a market, including high initial costs, licensing requirements, and strong brand loyalty among consumers.
Competitive Price-searcher
A market structure where firms set their prices and output levels to compete for consumers in a market with many sellers and product differentiation.
Long-run Equilibrium
A state in which all aspects of the market, including supply, demand, and price, are stabilized over time, allowing for full adjustment to any economic changes.
MR = MC
This equation represents the profit-maximizing condition in economics where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC), often used to determine the optimal level of output.
Q21: Single linkage can be used to measure
Q27: SMED establishes ways to eliminate unnecessary housekeeping
Q34: Referring to Scenario 17-2, the Middle East
Q40: Referring to Scenario 16-11, based on the
Q41: The SS method establishes ways to eliminate
Q90: Collinearity is present if the dependent variable
Q92: Referring to Scenario 16-5, the number of
Q125: Which of the following is not part
Q159: Total Productive Maintenance focuses on methods that
Q211: Referring to Scenario 18-12, what is the