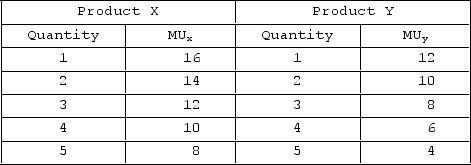
 The table shows the marginal utility schedules for old product X and new product Y for a hypothetical consumer. The price of X is $2, and the price of good Y is $1. The budget of the consumer is $10. If the consumer buys both old product X and new product Y, how much will the consumer buy of each to maximize utility?
The table shows the marginal utility schedules for old product X and new product Y for a hypothetical consumer. The price of X is $2, and the price of good Y is $1. The budget of the consumer is $10. If the consumer buys both old product X and new product Y, how much will the consumer buy of each to maximize utility?
Definitions:
Mutually Exclusive
Events or projects that cannot both occur at the same time, where the selection of one excludes the possibility of the other.
Independent
Not influenced or controlled by others in matters of opinion, conduct; not depending on another's authority.
Return on Assets
A financial ratio that shows the percentage of profit a company earns in relation to its overall resources (total assets).
Net Present Value
In capital budgeting, this refers to the variance between the current value of incoming cash and the current value of outgoing cash across a specific period, utilized to determine an investment's profit potential.
Q64: The change in a firm's total revenue
Q98: An example of derived demand in the
Q110: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8602/.jpg" alt=" In the graph,
Q141: Unlike a monopoly, an oligopoly tends to
Q186: The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive
Q202: A sequential game can be modeled in
Q224: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8602/.jpg" alt=" Use the graph
Q236: A simultaneous game is said to exist
Q244: The marginal productivity theory of income distribution
Q247: A firm decides to make a $40