Simplify.
-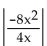
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The market price at which the quantity of goods supplied is equal to the quantity of goods demanded.
Nonprice Rationing
The allocation of goods or services using criteria other than price, such as waiting lists or lotteries.
Ration Coupons
Tokens or certificates that allow the holder to purchase a certain amount of a specific product, typically used during shortages or in a controlled economy.
Price Floor
A government or regulatory-imposed minimum price that can be charged for goods and services, typically above the equilibrium price, to prevent market prices from falling too low.
Q2: Why is economics a science of choices
Q10: Are strikes inefficient for the union and
Q10: Explain why most market labor supply curves
Q13: Analyze this statement: "U.S. tariffs on imported
Q25: 3x - 2y = -5 2x +
Q45: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A) [2, 6]
Q49: x + 2y + 2z = 0
Q51: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q66: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q106: 4 x - y = 19 5x