Multiply and simplify. Assume no radicands were formed by raising negative numbers to even powers.
-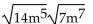
Definitions:
Normality
A statistical condition where data is symmetrically distributed around the mean, following a bell-shaped curve known as the normal distribution.
Null Hypothesis
The default hypothesis that there is no significant difference or relationship between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
Directional Alternative
A hypothesis that outlines the anticipated direction in the variation or association among variables.
T-statistic
A T-statistic is used in statistical testing to determine the significance of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the spread or variability of their scores.
Q28: -10 ·4<br>A) -40<br>B) -44<br>C) -30<br>D) 30
Q41: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A) 4, 49
Q128: 9i(2 - 5i)<br>A) 18i - 45<br>B) <img
Q199: b = 1, c = <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg"
Q224: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q241: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q244: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q285: x = -7.2<br>A) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt="x =
Q299: ( <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8504/.jpg" alt="( A)
Q351: s(t9) as 9(ts)