Scenario 9-2
• For a small country called Boxland,the equation of the domestic demand curve for
cardboard is  ,
,
where 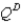 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and 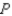 represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
• For Boxland,the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 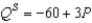 ,
,
where 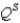 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and 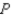 again
again
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2.If Boxland prohibits international trade in cardboard,then the equilibrium price of a ton of cardboard is
Definitions:
Immediate Predecessors
In project management and scheduling, tasks that directly precede another task, with no other tasks intervening.
Minimum Duration
The shortest time frame within which a particular task or project can be completed without delays.
Activity Duration
The time period required to complete a specific task or activity in a project.
Crash Cost
The additional costs incurred to reduce the completion time of a project or an activity, typically beyond standard operation costs.
Q12: What economic argument suggests that if transactions
Q35: The problem with the protection-as-a-bargaining-chip argument for
Q90: Refer to Figure 9-17.When the country moves
Q125: Refer to Figure 10-9.Which graph represents a
Q280: Refer to Figure 9-20.From the figure it
Q307: Which of the following would not be
Q355: Refer to Figure 9-11.Producer surplus in this
Q365: If Honduras were to subsidize the production
Q374: Refer to Scenario 9-1.If trade in peaches
Q417: Externalities tend to cause markets to be<br>A)