Table 13-14
Listed in the table are the long-run total costs for three different firms.
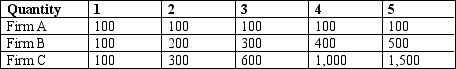
-Refer to Table 13-14.Which firm is experiencing constant returns to scale?
Definitions:
Allocative Efficiency
A state of the economy in which production is in accordance with consumer preferences; every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a utility to consumers equal to the cost of producing it.
Consumer Surplus
The difference in the amount consumers are prepared and have the means to pay for a service or good compared to the amount they actually do pay.
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good versus what they actually receive, often depicted as the area above the supply curve and below the market price.
Average Cost
The total cost of production divided by the number of goods produced; also known as per unit cost.
Q96: Economic profit is greater than or equal
Q180: Refer to Table 13-9.What is the variable
Q202: A firm's total profit equals its marginal
Q277: A seller in a competitive market<br>A) can
Q280: Refer to Figure 13-3.Which of the following
Q356: Refer to Figure 13-8.Quantity C represents the
Q366: Refer to Figure 13-5.Curve D intersects curve
Q394: Consider a competitive market with a large
Q401: Refer to Figure 14-6.Firms will be encouraged
Q486: Diseconomies of scale occur when<br>A) average fixed