Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The town's weekly demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is shown in the table below: 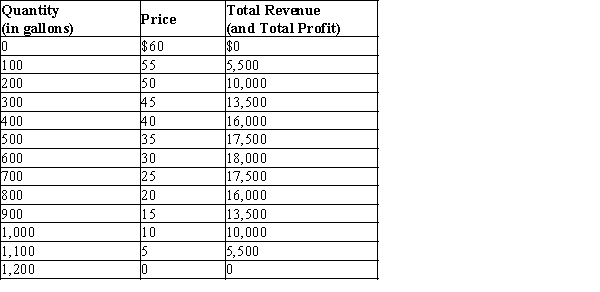
-Refer to Table 17-1. If Rochelle and Alec operate as a profit-maximizing monopoly in the market for water, how many gallons of water will be produced and sold?
Definitions:
Price Elasticity
A metric assessing the reaction of the amount of a good demanded to its price alterations.
Demand Function
An equation that describes the relationship between the quantity of a product demanded and the product’s price.
Price Elasticity
A measure in economics to show how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good, indicating its responsiveness to price changes.
Demand Function
A mathematical expression that shows the relationship between the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
Q40: Refer to Figure 17-4.If this game is
Q58: When all firms choose their best strategy
Q108: Which of the following is an example
Q118: Diminishing marginal product is closely related to<br>A)
Q152: Tying can be thought of as a
Q157: Refer to Table 17-9.If Acme and Pinnacle
Q177: Monopolistically competitive firms have excess capacity.To maximize
Q272: Total income in the United States is
Q280: When prisoners' dilemma games are repeated over
Q395: One thing that both critics of advertising