Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The town's weekly demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is shown in the table below: 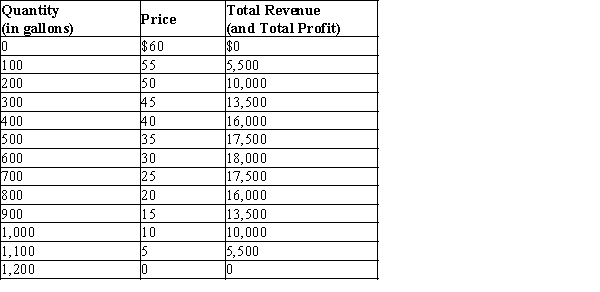
-Refer to Table 17-1. If this market for water were perfectly competitive instead of monopolistic, what price would be charged?
Definitions:
Nonexcludable
A characteristic of public goods where it is not possible to prevent individuals from using the good or service, regardless of whether they have paid for it.
Free-rider Problem
A situation in which some individuals benefit from resources or services without paying for them, leading to underprovision of those goods or services.
Marginal Private Benefit
The additional benefit received by the consumer or producer from consuming or producing one more unit of a good or service.
Marginal Social Cost
The additional cost imposed on society as a whole from producing one more unit of a good or service.
Q21: Refer to Table 16-6.Given the cost and
Q35: When McDonald's opens a store in Dhaka,Bangladesh,it
Q115: Refer to Table 17-11.Pursuing its own best
Q158: If the output effect from increased production
Q232: Refer to Table 17-1.If the market for
Q265: As the number of firms in an
Q353: Refer to Figure 17-1.Suppose this market is
Q394: Refer to Table 17-21.If Paul chooses Drive
Q426: Refer to Figure 16-8.In response to the
Q486: Refer to Figure 16-4.Which of the graphs