Table 17-3. The information in the table below shows the total demand for premium-channel digital cable TV subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each digital cable TV operator pays a fixed cost of $200,000 (per year) to provide premium digital channels in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the premium channel service to a household is zero.
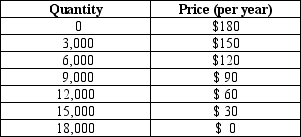
-Refer to Table 17-3.Assume there are two profit-maximizing digital cable TV companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of premium digital channel subscriptions to sell.How many premium digital channel cable TV subscriptions will be sold altogether when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium?
Definitions:
Frequency Marketing
A marketing strategy that rewards customers for frequent purchases or engagements with a brand, encouraging loyalty.
Usage Rate
The frequency at which a consumer uses a product or service, often influencing marketing strategies and segmentation.
Hotel Programs
Initiatives or loyalty schemes offered by hotels to reward frequent guests and enhance their staying experience.
Behavioral Segmentation
The method of segmenting a market into categories based on consumer awareness, perceptions, applications, or reactions towards a product.
Q42: Refer to Figure 18-3.Suppose that the price
Q59: The Sherman Antitrust Act was passed in<br>A)
Q178: Most of the total income earned in
Q199: Refer to Figure 16-9.When the firm is
Q207: A central issue in the Microsoft antitrust
Q247: Refer to Table 17-19.What is the Nash
Q289: In a monopolistically competitive market,the demand curves
Q301: Refer to Figure 16-4.Which of the panels
Q318: When a firm operates with excess capacity,it
Q374: Refer to Scenario 17-4.What will these two