Table 22-3
The citizens of Anytown will decide whether to build a new library, a new community center, or a new ice rink. Exactly one of the three choices will prevail, and the choice will be made by way of pairwise voting, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The preferences of the voters are summarized in the table below.
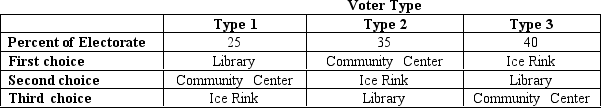
-Refer to Table 22-3.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the Condorcet paradox and the results of pairwise voting in Anytown?
Definitions:
Classical Conditioning
A psychological process through which associations between a previously neutral stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus are learned, leading to a learned response.
Premack Principle
A principle of reinforcement which states that a more probable behavior can reinforce a less probable behavior.
Law of Effect
A psychological principle stating that behaviors followed by satisfying consequences tend to be repeated, while those followed by unpleasant consequences are less likely to be repeated.
Cognitive Model
A theoretical approach that explains psychological phenomena by emphasizing mental processes, including perception, memory, and thought.
Q32: In cystic fibrosis the transport channels for
Q32: How many neutrons are in a neutral
Q63: Pedro,who knows nothing about construction,paid Benito to
Q88: Answer the following questions based on the
Q169: Two economists found empirical evidence that when
Q174: Refer to Figure 21-13.As the consumer moves
Q243: Signaling is an action taken by an
Q253: Pepsi and pizza are normal goods.When the
Q319: At a consumer's optimal choice,the consumer chooses
Q368: Refer to Figure 21-15.The price of X