What is the name of the following amino acid? 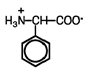
Definitions:
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds between molecules or within them, involving a hydrogen atom and a more electronegative atom, important in the structure of DNA and proteins.
Secondary Structure
The level of protein structure describing the regular local structures formed by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amide and carboxyl groups, such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
Hydrophilic End
The part of a molecule that is attracted to water and can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, often found in compounds like detergents.
Phospholipids
A group of fats that play a crucial role in the structure of all cellular membranes due to their ability to create double-layered lipid barriers.
Q1: Calcium is a mineral that is required
Q2: What starting material is necessary to complete
Q8: A complementary strand (written in the 5'-3'
Q15: The isoelectric point of an amino acid
Q16: Because many amino acids, fatty acids and
Q30: When enzyme activity is graphed versus the
Q47: Enzyme synthesis is controlled by the genetic
Q58: The simplest of the carboxylic acids is
Q77: The function of the mRNA molecule is
Q90: Amphetamines have structures similar to that of