Figure 10-2
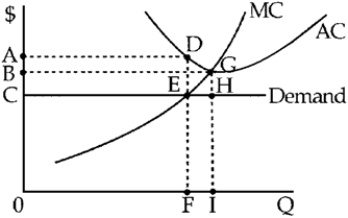
-In the short run, perfectly competitive firms will determine whether to continue producing the current output, reduce output, or increase output based on the relationship between
Definitions:
Marginal Cost Function
A mathematical representation showing how the cost of producing one additional unit of a good changes as production volume changes.
Optimal Output
The level of production that maximizes a firm’s profit or minimizes its cost under given conditions.
Profit
The financial gain acquired when the revenue generated from business activities exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes needed to sustain the activity.
Industry Supply Curve
A graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the total output of the industry for that good.
Q20: The supply curve for a perfectly competitive
Q35: Since a monopolist has a unique product,
Q63: At a firm's profit-maximizing level of output,
Q104: Figure 10-1 <br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX9061/.jpg" alt="Figure 10-1
Q112: A corporation's income is taxed<br>A)immediately after it
Q155: Double taxation is a problem for corporations.
Q189: The market demand curve in perfect competition
Q209: The necessity for choice, in economics, arises
Q215: The assignment of inputs to specific industries
Q231: Under the theory of perfect competition, firms