Figure 3-22 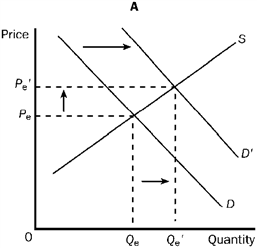
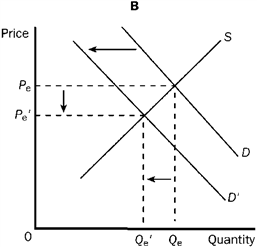
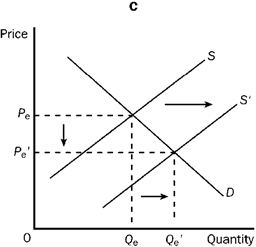
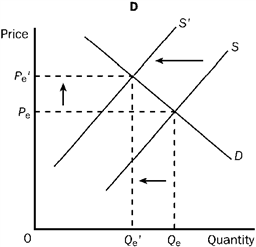
Refer to Figure 3-22. Graph C shows which of the following?
Definitions:
Incentive Function
The role of rewards or penalties in motivating individuals or entities to behave in certain ways.
Rationing Function
The ability of market prices to allocate scarce resources among competing uses, ensuring that only those willing and able to pay the price can obtain the good or service.
Equilibrium Economic Rent
The additional income received by a factor of production, due to its scarcity or unique value, when the market is in equilibrium.
Farmland
Land dedicated to agricultural practices including the cultivation of crops and raising livestock, a critical resource for food production.
Q3: Which of the following will most likely
Q77: Other things constant, which of the following
Q86: The law of demand refers to the<br>A)
Q107: Savannah is an attorney and also an
Q238: An airline ticket from Baltimore to Miami
Q243: Figure 4-21 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX9057/.jpg" alt="Figure 4-21
Q252: Keri decided to sleep in today rather
Q352: How would a decrease in consumer income
Q374: In the textbook market, a rise in
Q541: When experts first predicted major weather-related coffee