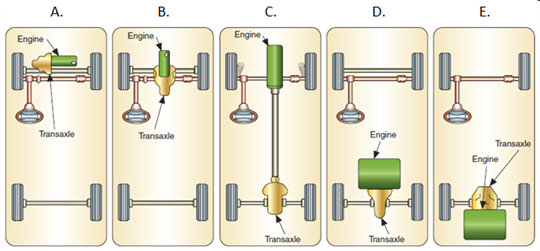
This figure shows five different ways to configure a transaxle system. Briefly describe the positions of the engine and transaxle in each configuration.
Definitions:
Dendritic Branching
The process by which neurons' dendrites grow and expand to increase synaptic connections.
Hippocampus
A major component of the brain in the temporal lobe involved in memory formation and spatial orientation.
NMDA Receptor
A type of receptor involved in synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and is critical for excitatory neurotransmission in the brain.
Postsynaptic Membrane
The specialized area of a cell membrane on a neuron that receives and processes signals from another neuron at a synapse.
Q1: The _, often referred to as the
Q14: Briefly distinguish between a 4 × 2
Q21: The most common file type of media
Q21: The operator with the highest order of
Q23: A two-piece drive shaft is also referred
Q23: Instead of eyeballing the controls on the
Q30: Distinguish between an integral carrier housing and
Q31: The property that connects a Spinner control
Q33: The bearing of a _ is located
Q35: The spring used in most pressure plates