For the triangle described below, solve for B and use the results to explain why the triangle has two solutions. 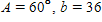 ft,
ft, 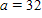 ft
ft
Definitions:
Slippery Slope Fallacy
A logical fallacy in which a relatively small first step leads to a chain of related events culminating in some significant effect, much like sliding down a slippery slope.
Gambler's Fallacy
A logical fallacy in which one assumes that future probabilities are altered by past events, often seen in gambling when assuming a certain outcome is "due".
Sunk Cost Fallacy
The misconception of valuing a project or investment based on the amount of resources already invested, rather than the prospective future returns.
Argumentum Ad Hominem
A logical fallacy that occurs when an argument is rebutted by attacking the character, motive, or other attribute of the person making the argument, rather than addressing the substance of the argument itself.
Q3: The Universe consists of the Sun, its
Q21: Solve the equation for θ if <img
Q33: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX9354/.jpg" alt="If with
Q47: From the list below find the expression
Q65: Draw the vector V that goes from
Q87: If z is a complex number, show
Q109: Use your graphing calculator to convert the
Q112: Find three cube roots for the complex
Q147: Simplify the expression. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX9354/.jpg" alt="Simplify the
Q196: The area of a triangle is 45