When a force F stretches a rope of mass per unit length ρ , the velocity of a wave in the rope is given by 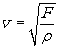
You pull on a rope with a certain force, and a wave travels in the rope with a certain velocity. If you double your force, the velocity of a wave in the rope is now 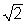 times the original velocity.
times the original velocity.
Definitions:
Overhead Assigned
Refers to the allocation of indirect costs to products, services, or cost centers.
Product U4
Product U4 is a designated name for a specific product, possibly indicating its position or type within a wider range of products offered by a company or manufacturer.
Traditional Costing
A costing methodology that assigns overhead costs to products based on a predetermined rate, often using direct labor hours as the allocation base.
Activity-Based Costing
Activity-Based Costing is a method of allocating overhead to specific products or services based on the activities that contribute to overhead costs.
Q9: The highest frequency visible light is<br>A) violet.<br>B)
Q26: A heater is rated at 1200 watts
Q32: Consider a situation where two moving objects
Q51: The energy stored in a stretched spring
Q60: Two pistons push down on the fluid
Q106: An atomizer works because of<br>A) Archimedes' principle.<br>B)
Q108: The direction of a magnetic field at
Q117: Superconductivity is lost when a certain critical
Q133: As the air cools at night the
Q137: A magnetic field exerts a force on