The cost of controlling emissions at a firm goes up rapidly as the amount of emissions reduced goes up. Here is a possible model: 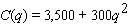 where q is the reduction in emissions (in pounds of pollutant per day) and C is the daily cost (in dollars) of this reduction. Government clean-air subsidies to the firm are based on the formula
where q is the reduction in emissions (in pounds of pollutant per day) and C is the daily cost (in dollars) of this reduction. Government clean-air subsidies to the firm are based on the formula 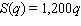 where q is again the reduction in emissions (in pounds per day) and S is the subsidy (in dollars) . Calculate the net cost function
where q is again the reduction in emissions (in pounds per day) and S is the subsidy (in dollars) . Calculate the net cost function 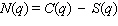 given the cost and subsidy above, and find the value of q that gives the lowest net cost. What is this lowest net cost?
given the cost and subsidy above, and find the value of q that gives the lowest net cost. What is this lowest net cost?
Definitions:
Neo-Marxism
A strand of Marxist theory that combines elements of traditional Marxism with other intellectual traditions such as critical theory, aiming to update and reinvigorate Marxist analysis for contemporary conditions.
World-Systems Theory
A multidisciplinary approach to world history and social change that suggests there is a world economic system in which some countries benefit while others are exploited.
Historical Oriented Marxism
Historical Oriented Marxism is an approach within Marxist theory that emphasizes the historical and materialist analysis of societal development, class struggle, and social change.
Hegelian Marxists
Marxists who incorporate elements of Hegel's philosophy, focusing on dialectical methods and contradictions within society.
Q34: Calculate the 5-unit moving average of the
Q38: Evaluate the integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8650/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q50: Use logarithms to solve the equation. (Round
Q55: Find the total value of the given
Q60: Which of the following commands is used
Q82: How long, to the nearest year, will
Q93: Calculate the limit algebraically. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8650/.jpg" alt="Calculate
Q100: Calculate the average rate of change of
Q106: The estimated marginal revenue for sales of
Q129: The cost of controlling emissions at a