The normal distribution curve, which models the distributions of data in a wide range of applications, is given by the function 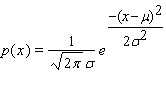
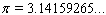 and
and 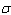 and
and 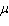 are constants called the standard deviation and the mean, respectively. With
are constants called the standard deviation and the mean, respectively. With 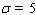 and
and 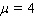 , approximate
, approximate 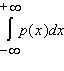 .
.
Definitions:
Common Stock
A type of equity security that represents ownership in a corporation and gives shareholders voting rights, often with the potential for dividends.
Acid-Test Ratio
A financial metric that assesses a company's ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its most liquid assets.
Company
A business entity established by a collection of people to conduct and manage an enterprise, whether it's for commercial or industrial purposes.
Current Ratio
A measure of a corporation's capability to meet obligations due in less than one year, found by dividing its total current assets by its total current liabilities.
Q6: A venture opportunity screening is the same
Q8: Calculate the average rate of change of
Q13: Mark Twain once said, "I was always
Q34: The FeatureRich Software Company sells its graphing
Q44: Determine the cost of goods sold for
Q65: A sound business model is a plan
Q68: Find all the values of x (if
Q105: Find the derivative of the function. <img
Q108: Find all points of discontinuity of the
Q130: Calculate the limit algebraically. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8650/.jpg" alt="Calculate