The cost of controlling emissions at a firm goes up rapidly as the amount of emissions reduced goes up. Here is a possible model. 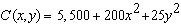 where x is the reduction in sulfur emissions, y is the reduction in lead emissions (in pounds of pollutant per day) , and C is the daily cost to the firm (in dollars) of this reduction. Government clean-air subsidies amount to $200 per pound of sulfur and $50 per pound of lead removed. How many pounds of pollutant should the firm remove each day to minimize the net cost (cost minus subsidy) ?
where x is the reduction in sulfur emissions, y is the reduction in lead emissions (in pounds of pollutant per day) , and C is the daily cost to the firm (in dollars) of this reduction. Government clean-air subsidies amount to $200 per pound of sulfur and $50 per pound of lead removed. How many pounds of pollutant should the firm remove each day to minimize the net cost (cost minus subsidy) ?
Definitions:
Economical
Pertaining to efficient use or management of resources to prevent wasteful expenditures.
Wheel of Retailing
is a concept that illustrates how new retailing forms often start at a low price point with minimal services before evolving into more established forms with higher costs and services.
Competitive Foothold
A strategic position obtained by a company in a market that gives it an advantage over its competitors.
Wholesalers
Entities that sell products in large quantities, typically to retailers or other intermediaries, rather than to the final consumer.
Q8: Based on the 2018 tax laws, the
Q11: Find the exact location of all the
Q32: Calculate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8650/.jpg" alt="Calculate .
Q43: Venture opportunity screening involves assessment of an
Q71: The "dot.com" or Internet bubble burst in
Q74: Find the indicated derivative. The independent variable
Q75: Compute the derivative function <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8650/.jpg" alt="Compute
Q76: The first component of a sound business
Q77: If you invest $20,000 at 9% interest
Q81: An innovation that creates a new market