Three possible resonance forms for NO₂ NH - are shown below. Pick the best answer.
I. 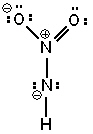
II. 
III. 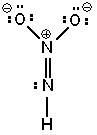
Definitions:
Sensorineural Deafness
A type of hearing loss resulting from damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or to the nerves that connect the ear to the brain.
Selective Deafness
A psychological condition where an individual may unconsciously ignore or not process auditory information or sounds that they find distressing or overwhelming.
Feature Detectors
Feature detectors are specialized neurons in the brain that identify specific elements of a sensory input, such as edges, lines, or movements, helping to interpret complex stimuli.
Weber's Constant
A principle in psychology that quantifies the perception of change in a given stimulus, stating that the ratio of the increment threshold to the background intensity is constant.
Q5: Which of the following defines the heat
Q5: How many valence electrons are present in
Q34: What is the vapor pressure lowering ,
Q47: How many unpaired electrons are present in
Q56: Which of the following molecules would have
Q78: Given the three statements below, pick the
Q90: What is the mole fraction of water
Q122: What type of hybrid orbitals are used
Q166: Which aqueous solution would be predicted to
Q167: The solubility of a gas in water