The greatest common factor of the binomial 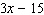 is
is 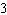 . The greatest common factor of the binomial
. The greatest common factor of the binomial 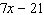 is
is 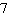 . What is the greatest common factor of their product,
. What is the greatest common factor of their product, 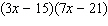 , when it has been multiplied out?
, when it has been multiplied out? 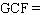 __________
__________
Definitions:
High-quality Relationship
A profound and positive connection between individuals characterized by trust, respect, and mutual understanding.
LMX Studies
Research concentrated on exploring the dynamics of the leader-member exchange theory, particularly how these interactions influence organizational outcomes.
In-groups
Social groups with which an individual identifies, often characterized by a high degree of loyalty and common interests among its members.
Out-groups
Individuals or subgroups within an organization or society that are not part of the dominant group or in-crowd, often experiencing exclusion.
Q6: Divide. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Divide. A)
Q19: Graph the solution set. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Graph
Q25: Factor the trinomial. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Factor the
Q77: A boat travels 28 miles up the
Q87: Simplify the complex fraction. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Simplify
Q122: Multiply the expressions. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Multiply the
Q137: Reduce the following rational expression to lowest
Q178: Factor the expression as the sum or
Q197: Solve the following equation. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Solve
Q226: Perform the indicated operations. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8808/.jpg" alt="Perform