Read the scale. 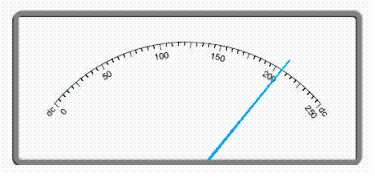 __________ V
__________ V
Definitions:
Decision Making
The cognitive process of selecting a course of action among various alternatives, often involving a balance of risk and reward.
Neoclassical Economics
The dominant and conventional branch of economic theory that attempts to predict human behavior by building economic models based on simplifying assumptions about people’s motives and capabilities. These include that people are fundamentally rational; motivated almost entirely by self-interest; good at math; and unaffected by heuristics, time inconsistency, and self-control problems.
Behavioral Economics
The branch of economic theory that combines insights from economics, psychology, and biology to make more accurate predictions about human behavior than conventional neoclassical economics, which is hampered by its core assumptions that people are fundamentally rational and almost entirely self-interested. Behavioral economics can explain framing effects, anchoring, mental accounting, the endowment effect, status quo bias, time inconsistency, and loss aversion.
Rational Decision Making
A systematic process of defining problems, evaluating alternatives, and choosing the most optimal solution based on logical and analytical reasoning.
Q8: Read the measurement shown on the vernier
Q15: Solve the triangle using the labels
Q30: The resistor current is 50.2 A. The
Q33: Solve the triangle given below. Do not
Q46: Follow the rules for working with measurements.
Q93: Read the measurement shown on the U.S.
Q183: Find the measure of the missing angle
Q190: The measurement is 34 km. Find the
Q197: Follow the rules for working with
Q198: Read the measurement shown on each vernier