An 83-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department due to chest pressure accompanied by nausea and vomiting. She felt well until 3 days ago when she was watching television and experienced substernal chest discomfort that radiated to her back. The pain lasted nearly an hour before resolving spontaneously; she also had nausea and vomiting at that time. The patient has never had chest pain before and has had no further discomfort since. She attributes the entire experience to drinking expired milk. The patient is currently without symptoms but is seen in the emergency department at the insistence of her daughter, who is a physician. Other medical problems include overactive bladder and osteoarthritis. Medications include oxybutynin and ibuprofen as needed.
Blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg, pulse is 61/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient is in no acute distress. Jugular venous pulsations are normal. Lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Apical impulse is normal. No heart murmurs are heard. Pulses are 2+ and symmetrical. There is no edema.
ECG shows normal sinus rhythm with 2-mm Q waves in leads II, III, and aVF. Laboratory results are as follows: The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit and scheduled for coronary angiography. Shortly after arriving on the floor, she is noted to be markedly dyspneic. Repeat blood pressure is 90/45 mm Hg, pulse is 125/min, and respirations are 20/min. Lung examination reveals bilateral diffuse crackles. A pulmonary arterial catheter is placed, with the results shown below.
The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit and scheduled for coronary angiography. Shortly after arriving on the floor, she is noted to be markedly dyspneic. Repeat blood pressure is 90/45 mm Hg, pulse is 125/min, and respirations are 20/min. Lung examination reveals bilateral diffuse crackles. A pulmonary arterial catheter is placed, with the results shown below.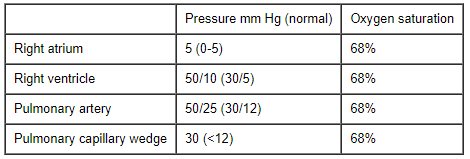 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Definitions:
Essential Resource
A fundamental input or asset that is necessary for the production processes or for sustaining life and economic activities.
Taxi Cabs
Licensed vehicles for hire that provide passenger transport services for a fare, traditionally hailed on the street or booked in advance.
Cab Fares
Charges levied for the service of transporting individuals in taxicabs, typically based on distance traveled and time taken.
Operating Cost
Expenses associated with the day-to-day functioning of a business, such as rent, utilities, and salaries.
Q1: Perform the operation. Write the answer in
Q7: Find the square root without using a
Q8: The analysis section includes the issue, rule
Q15: Tell whether the ordered pair (- 5,
Q15: The initials of the typist are usually
Q16: The components and considerations involved in the
Q17: Simplify the expression. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8672/.jpg" alt="Simplify the
Q43: A 75-year-old man with a history of
Q432: A 74-year-old man is admitted to the
Q724: A 72-year-old woman comes to the office