An 85-year-old nursing home resident is brought to the emergency department due to worsening cough, difficulty breathing, and decreased responsiveness for 3 days. Medical conditions include hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and dementia. Following evaluation that reveals leukocytosis and lung infiltrates, the patient's respiratory distress progressively worsens. Endotracheal intubation is performed; mechanical ventilation is begun; the patient is given intravenous fluids and antibiotics; a central venous catheter is placed; and she is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) .
In the ICU, the patient requires increasing ventilatory support with elevated airway pressures. Temperature is 35.6 C (96 F) , blood pressure is 84/40 mm Hg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry shows 92% on assist-control mode with a tidal volume of 300 mL, fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) of 60%, and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 5 cm H2O. Examination reveals decreased breath sounds on the right, rhonchi on the left, and normal S1 and S2. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is no extremity edema.
Arterial blood gases and chest x-ray are shown below.
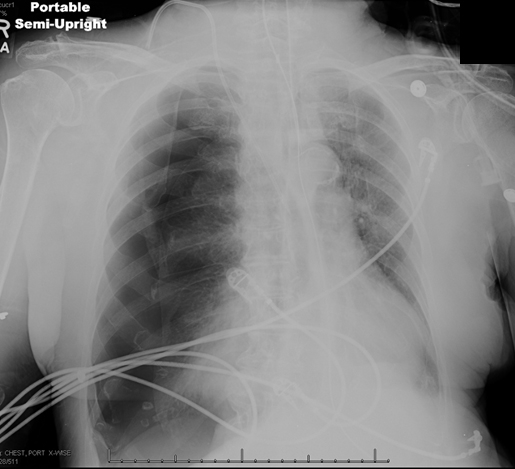
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Definitions:
HCPCS Level II
A standardized coding system used in the United States to classify healthcare services, supplies, and procedures not covered by the standard medical coding system.
Alphabetic Characters
Letters in the alphabet, used in the construction of words, including both lowercase and uppercase forms.
Global Period
The period of time that is covered for follow-up care of a procedure or surgical service.
Applicable Modifiers
Specific codes or signals used in medical billing to indicate that a service or item has been altered in some way without changing the definition.
Q9: When a court in State A looks
Q10: One of the objects of legal analysis
Q74: A 67-year-old man is brought to the
Q93: A 79-year-old nursing home resident is admitted
Q390: A 69-year-old man comes to the office
Q416: A 57-year-old woman undergoes mitral valve replacement
Q542: An 80-year-old hospitalized woman is evaluated for
Q577: A 22-year-old African American man is evaluated
Q632: A 36-year-old woman comes to the office
Q884: A 76-year-old man comes to the office