A 60-year-old man with alcoholism is admitted after being found unresponsive in the street. No other history is available.
His temperature is 37.1 C (98.8 F) , blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and regular, and respirations are 20/min. On examination, the patient is disheveled and appears chronically ill. He has decreased muscle mass and no subcutaneous fat. He responds to painful stimuli and has slurred speech. Carpal spasm was noted in the hand of the arm in which his blood pressure was taken. Mucous membranes are dry and there is no moisture in the axillae. He has nystagmus on end lateral gaze of both eyes. No other focal neurologic findings are present.
Laboratory results are as follows:
Intravenous thiamine and fluids consisting of 3 L normal saline/5% dextrose containing 40 mEq of potassium are administered over 4 hours. Electrolytes are re-measured with the following results: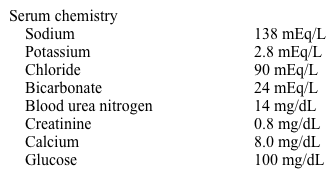
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypokalemia?
Definitions:
Alcohol
A psychoactive substance found in beverages such as beer, wine, and spirits, which can affect the central nervous system, leading to intoxication and, with excessive consumption, addiction.
Depressants
A class of drugs that reduce neurological function, leading to calming, sedative effects, or decreased awareness.
Neural Activity
The operation of nerve cells (neurons) which involves the generation and transmission of electrical and chemical signals.
Caffeine
A stimulant found in coffee, tea, and various other beverages that affects the central nervous system, resulting in increased alertness and reduced fatigue.
Q7: In a lawsuit, a fact is information
Q15: It is not appropriate to list key
Q50: A 52-year-old woman develops cardiac arrest while
Q114: A 65-year-old man is brought to the
Q128: A 36-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q232: A 36-year-old man comes to the physician
Q301: A 63-year-old man comes to the physician
Q404: A 40-year-old woman is evaluated for mildly
Q718: A 36-year-old woman comes to the office
Q799: A 75-year-old woman is seen in consultation