A 65-year-old woman with a history of rheumatoid arthritis comes to the physician with persistent hand pain aggravated by use. She was prescribed tramadol and occupational therapy 1 year ago and has had no relief. Rheumatoid arthritis was diagnosed 20 years ago, and she was started on methotrexate, prednisone, and hydroxychloroquine at that time. She was prescribed etanercept 10 years ago and switched to adalimumab 5 years later due to persistent disease activity. The patient's other medical problems include hypertension and acid reflux disease. Her current medications include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, adalimumab, tramadol, prednisone, and ibuprofen. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs.
Her vital signs are normal. Musculoskeletal examination is notable for the presence of rheumatoid deformities in the hands (shown below) and feet. There is no joint tenderness or effusion. Neurological examination is within normal limits.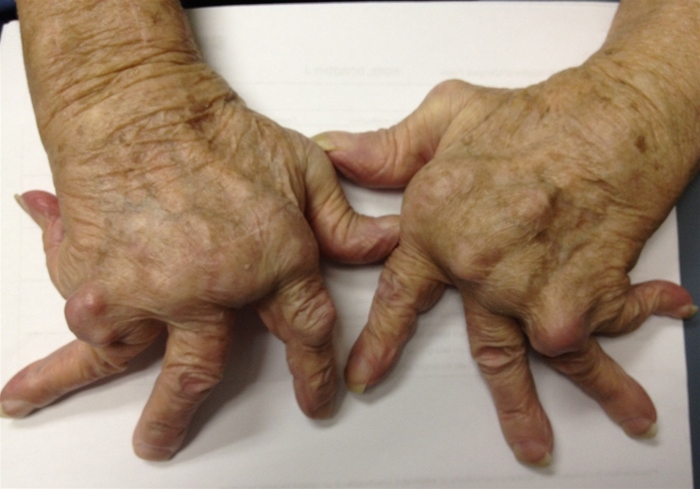
Laboratory results are as follows:
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Definitions:
Goal Setting Theory
A process theory that states that goals are motivational when they are specific and challenging, when organizational members are committed to them, and when feedback about progress toward goal attainment is provided.
ADHD
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by problems paying attention, hyperactivity, or impulsiveness that are not appropriate for a person's age.
Inattention
The lack of focus or concentration on a specific task or environment, often noted in various psychological diagnoses.
Hyperactivity
A condition characterized by overly active behavior that can include excessive talking, fidgeting, or difficulty remaining still and focused.
Q99: A 25-year-old woman comes to the office
Q105: Convert <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8673/.jpg" alt="Convert to
Q225: A 47-year-old previously healthy man comes to
Q251: Subtract the fractions. Reduce to simplest form.
Q324: A 28-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q463: A 63-year-old woman with a long history
Q549: A 30-year-old man comes to the office
Q580: A 40-year-old woman comes to the office
Q587: A 36-year-old woman with a history of
Q750: A 65-year-old man comes to the physician