An electronically controlled thermostat in a home is programmed to lower the temperature automatically during the night. The temperature T, in degrees Fahrenheit, is given in terms of t, the time on a 24 hour clock, as shown in the figure. The thermostat is then reprogrammed to produce a temperature H where . Explain how this changes the temperature of the house. 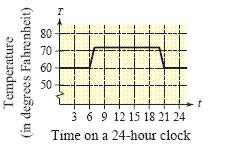
Definitions:
Conditioned Stimulus
Within classical conditioning, an initially neutral stimulus becomes linked with an unconditioned stimulus and ultimately elicits a conditioned response.
Neutral Stimulus
In conditioning, a stimulus that initially elicits no specific response other than focusing attention, which can eventually elicit a conditioned response when paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
Unconditioned Response
A natural, unlearned reaction to an unconditioned stimulus, part of classical conditioning theory.
Unconditional Reinforcement
A form of reinforcement in operant conditioning that is given consistently every time a desired response is made.
Q4: Graph the equation <span class="ql-formula"
Q12: Solve the equation. <span class="ql-formula"
Q24: Identify the center and radius of
Q33: Complete the table showing the equivalent
Q67: Determine the value of k such
Q95: Find the partial sum <span
Q101: The bill for repairing a car
Q102: The total amount of money accrued
Q107: Use synthetic division to divide.
Q155: Use a graphing calculator to find