A 65-year-old woman comes to the office reporting progressively increasing orthopnea, daytime fatigue, and morning headache for the last month. She has had no chest pain or problems with swallowing or speech. Medical conditions include myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F) , blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry shows 95% on room air. BMI is 24 kg/m2. Examination shows normal jugular venous pressure, clear lungs, and normal heart sounds. There is no peripheral edema. Neurologic examination shows 3/5 power in right lower extremity and 4/5 power in left lower extremity and muscle atrophy, unchanged from her last examination 2 months ago. Laboratory results are as follows: 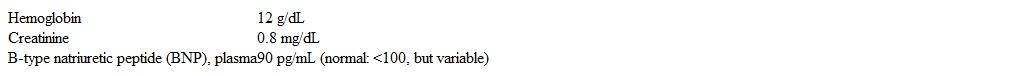 Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Definitions:
Axial Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that consists of the bones along the axis of the body, including the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
Facial Skeleton
The framework of bones that supports the face, including the jaw, cheekbones, and nasal bones.
Thoracic Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that comprises the ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum, providing protection and support to the thorax.
Appendicular Skeleton
The Appendicular Skeleton comprises the bones of the limbs and girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton, facilitating movement and supporting the weight of the body.
Q23: A 42-year-old man is admitted to the
Q110: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the
Q153: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the
Q444: A 58-year-old man comes to the office
Q512: A 63-year-old man is brought to the
Q1007: A 40-year-old man comes to the physician
Q1012: A 54-year-old man comes to the office
Q1292: A 30-year-old man comes to the office
Q1373: A 43-year-old man comes to the office
Q1655: A 45-year-old man is brought to the