Service Consumer A sends a message to Service A (1) , which then forwards the message to Service B (2) . Service B forwards the message to Service C (3) , which finally forwards the message to Service D (4) . Services A, B, and C each contain logic that reads the content of the message and, based on this content, determines which service to forward the message to. As a result, what is shown in the Figure is one of several possible runtime scenarios. 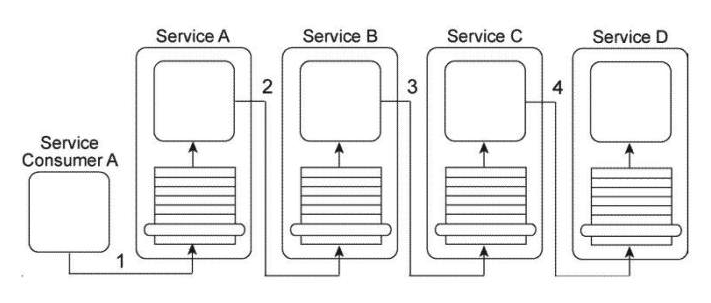 You are told that the current service composition architecture is having performance problems because of two specific reasons. First, too many services need to be explicitly invoked in order for the message to arrive at its destination. Secondly, because each of the intermediary services is required to read the entire message contents in order to determine where to forward the message to, it is taking too long for the overall task to complete. What steps can be taken to solve these problems without sacrificing any of the functionality that currently exists?
You are told that the current service composition architecture is having performance problems because of two specific reasons. First, too many services need to be explicitly invoked in order for the message to arrive at its destination. Secondly, because each of the intermediary services is required to read the entire message contents in order to determine where to forward the message to, it is taking too long for the overall task to complete. What steps can be taken to solve these problems without sacrificing any of the functionality that currently exists?
Definitions:
Reliability
The degree to which an assessment tool produces stable and consistent results over time.
Utility
A term used to describe services provided to the public, such as water, electricity, natural gas, and sewage treatment.
Intrusive Environment
A setting or situation where privacy is limited, and external factors significantly affect personal space or work conditions.
Q12: "A primary focus of service modeling is
Q14: When designing service-oriented architectures, it is important
Q21: Black Box testing determines whether combinations of
Q31: In which policies the contract provides for
Q34: The role of the facilitator is:<br>A) To
Q36: A customer using SnowSQL / native connectors
Q41: Which of the following will NOT generate
Q61: _ allow investments to be made, up
Q66: Pick the best tactic to use in
Q93: You are monitoring your Internet connection, and