Service A is a utility service that provides generic data access logic to a database that contains data that is periodically replicated from a shared database (1) . Because the Standardized Service Contract principle was applied to the design of Service A, its service contract has been fully standardized. The service architecture of Service A is being accessed by three service consumers. Service Consumer A accesses a component that is part of the Service A implementation by invoking it directly (2) . Service Consumer B invokes Service A by accessing its service contract (3) . Service Consumer C directly accesses the replicated database that is part of the Service A implementation (4) . You've been told that the shared database will soon be replaced with a new database product that will have new data models and new replication technology. How can the Service A architecture be changed to avoid negative impacts that may result from the replacement of the database and to establish a service architecture in which negative forms of coupling can be avoided in the future? 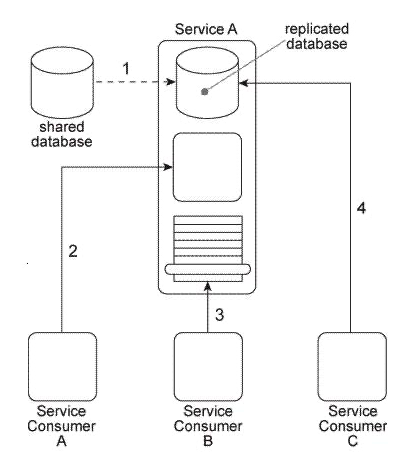
Definitions:
Gross Primary Productivity
The total rate at which an ecosystem's producers, like plants, convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of biomass.
Photosynthesis
A method by which plants and other organisms transform light energy, often from the sun, into chemical energy that can subsequently be utilized to power the organism's functions.
Third Trophic Level
The level in an ecosystem's food chain occupied by secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers.
Herbivore
An animal that feeds on plants or algae. Also called primary consumer.
Q5: A SOAP-based Web service is required to
Q24: Messages transmitted using WS-ReliableMessaging are typically _
Q25: In which account current, for individual policies,
Q29: An intermediary can be an initial sender
Q39: Your network has a few critical devices
Q46: Which method is called on a shipping
Q47: Which one of the following statements is
Q51: Official Endpoint is a compound pattern that
Q59: Which of the following statements is true?
Q210: Immunization theory says that:<br>A) duration matching requires