A company has deployed a four-node cluster in a COLO environment with server configurations listed below. The company wants to ensure there is 50% overhead for failover and redundancy. There are currently eight VMs running within the cluster with four vCPUs x32GB each. The company wants to better utilize its resources within the cluster without compromising failover and redundancy. 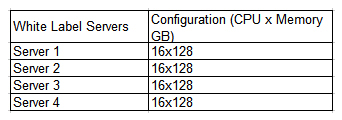 Given the information above, which of the following should a cloud administrator do to BEST accommodate failover and redundancy requirements?
Given the information above, which of the following should a cloud administrator do to BEST accommodate failover and redundancy requirements?
Definitions:
Nuclear Pores
Structures in the nuclear envelope that allow passage of certain materials between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm.
mRNA Transport
The process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where they can be translated into proteins.
Regulation of Chromatin
The process by which the structure and function of chromatin are controlled or influenced, affecting gene expression and DNA replication.
Heterochromatin
A tightly packed form of DNA, which comes in different varieties and is associated with regions of DNA that are gene-poor and transcriptionally inactive.
Q26: A cloud administrator configures a server to
Q48: A user's computer has been running slowly
Q63: A Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is
Q64: A security team wants to make SaaS
Q65: A security manager needed to protect a
Q67: The access control department creates a process
Q114: During the deployment of a new system,
Q221: Ann, a user, is doing her daily
Q258: A cloud provider wants to automate the
Q268: A company is seeking a new backup