Below is an illustration of the buccal surface of a mandibular right second molar. Structure "a" depicts the 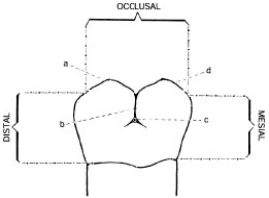
Definitions:
Axon
A long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
Synapse
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle where electrical or chemical signals are transmitted.
Soma
The cell body of a neuron, containing the nucleus and other structures essential to cell function.
Glial Cells
Non-neuronal cells in the central and peripheral nervous system that support and protect neurons, playing a key role in brain function.
Q1: Lining mucosa that extends beyond the area
Q5: Maxillary molars have three roots, a facial
Q6: Enamel pearls (select all that apply):<br>A) Are
Q7: Fordyce granules normally function as<br>A) Taste buds<br>B)
Q8: Both the corrugator and the platysma pull
Q13: The lateral pterygoid performs each of the
Q13: The permanent molars develop from successional lamina.
Q19: Development of the dentinocemental junction (DCJ) involves
Q22: In split brain patients, the corpus callosum
Q25: A patient complains of moderate pain in