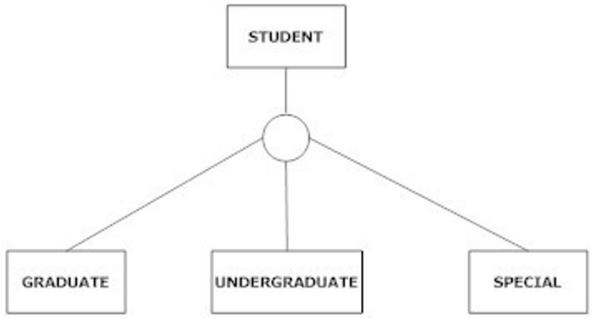
The following figure is an example of total specialization.
Definitions:
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing one additional unit of a product or service, crucial for decision-making about production levels and pricing.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of foregone alternatives when one choice is made over another, representing the benefits that could have been gained by choosing the next best alternative.
Purely Competitive
Refers to a market structure characterized by a large number of small firms, a homogeneous product, and very easy entry and exit.
Supply Curve
A chart that illustrates the connection between a product's price and the quantity that producers are ready to offer.
Q5: Databases were developed as the first application
Q12: The sort method rearranges the elements of
Q26: All of the following are common denormalization
Q28: The _ rule states that an entity
Q30: The third number in string slicing brackets
Q30: The following query totals sales for each
Q35: A referential integrity constraint is a rule
Q35: What will be assigned to s_string after
Q61: A relation is in first normal form
Q82: E. F. Codd developed the relational model