A branded store has outlets around the world that generates profit in the British pound, the New Zealand kiwi, and the Japanese yen. At the end of each quarter, the store converts the revenue from these three international outlets back into U.S. dollars, exposing itself to exchange rate risk. The current exchange rates are US$1.56 per £1, US$0.85 per NZD$1, and US$0.02 per ¥1. The management of the store wants to construct a simulation model to assess its vulnerability to uncertain exchange rate fluctuations. The quarterly profits earned in British pounds, New Zealand kiwis, and Japanese yen are £150,000, NZD$200,000, and ¥9,000,000, respectively. The data is given below.
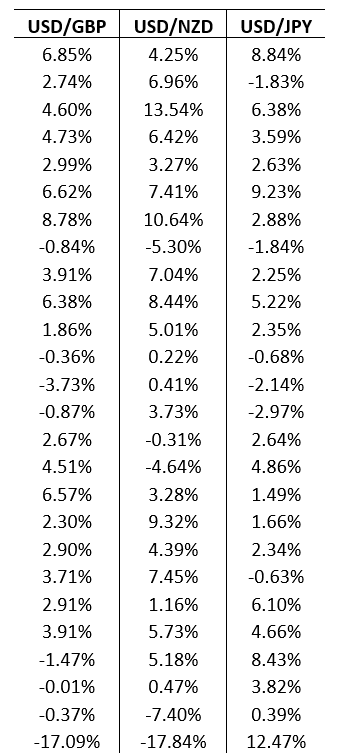
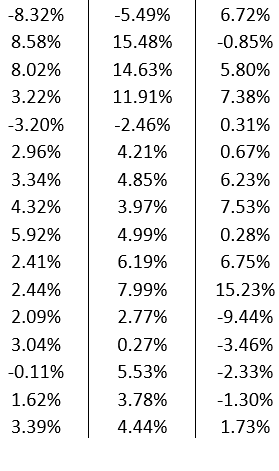
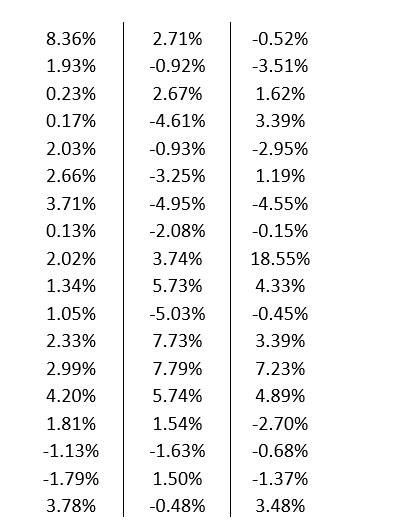
a. If exchange rates stay at their current values, what is the total quarterly profit in U.S. dollars?
b. Model the uncertainty in the quarterly changes of the exchange rates between U.S. dollars and British pounds, New Zealand kiwis, and Japanese yen using a SLURP. Use your simulation model to estimate the average total quarterly profit in U.S. dollars. What is the probability that the total quarterly profit will be lower than the answer in part a?
Definitions:
Rescindable
Refers to a contract or deal that can be legally canceled or revoked.
Voidable
A contract or act that is voidable can be legally declared invalid by one of the parties involved, often due to reasons such as fraud or coercion.
Implied-In-Law
A legal term referring to rights or obligations that are enforced by a court, not because of an agreement or contract, but to avoid injustice.
Implied-In-Fact
A contract formed by the circumstances or conduct of the parties involved, rather than written or spoken words.
Q3: Which of the following is a drug
Q9: Which of the following actions by a
Q10: One of the ways to use the
Q11: Which of the following medications are considered
Q15: The reduced gradient is analogous to the
Q18: A patient in a motor vehicle accident
Q20: The monthly sales (in hundreds of dollars)
Q24: Meperidine,75 mg IV push,is ordered by the
Q53: Develop a model that minimizes semivariance for
Q54: The data shown below are the average