If A is a
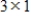 matrix, and B is an
matrix, and B is an
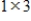 matrix, then
matrix, then
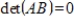
.
Definitions:
Positive Externalities
These are benefits that a transaction or activity provides to those not involved in the transaction or activity.
Negative Externalities
Costs suffered by a third party as a result of an economic transaction that they were not directly involved in.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages reaped by companies when production becomes efficient, typically resulting from increased production where the cost per unit of output drops as scale increases.
Public Goods
Goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning they are available to all and one person's use does not diminish another's.
Q8: A nondirectional alternative hypothesis for an independent
Q13: Suppose that A is a <br> <img
Q14: Use the Gram-Schmidt process to convert the
Q14: Use a system of linear equations to
Q15: Let A and B be <br> <img
Q17: If A is invertible, then <br> <img
Q24: Suppose matrix <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="Suppose matrix
Q26: The general solution to a linear system
Q44: The singular value decomposition of a matrix
Q47: Determine if the homogeneous system <br> <img