If
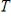 is a linear transformation, then
is a linear transformation, then
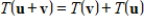 for all vectors
for all vectors
 and
and

.
Definitions:
Directional Hypothesis
A hypothesis that specifies the direction of the expected difference or relationship.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement suggesting that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations, representing a default position that there is no association between two measured phenomena.
Type II Error
The error made when a false null hypothesis is not rejected, missing the detection of a real effect.
Type I Error
The mistake of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
Q5: The FBI's COINTELPRO is an example of
Q6: If <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="If
Q7: Suppose <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="Suppose and
Q13: If A is a <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg"
Q14: If <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="If
Q30: Evaluate <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="Evaluate
Q35: If <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="If
Q35: Find an equation for the line in
Q40: If <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMC1039/.jpg" alt="If
Q57: Find the vector in the subspace S