Please use the following information to answer the following question(s) .
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm) , and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day) . The data you collected are as follows:
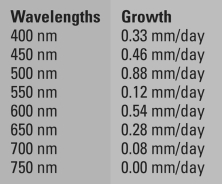
Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s) :
-Why do some plant species require shaded conditions while other plant species require bright sunlight?
Definitions:
Peripheral Nervous System
Part of the nervous system that consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Efferent Fibers
Nerve fibers that carry signals away from the central nervous system to the peripheral effectors, such as muscles and glands.
Cranial Nerves
Twelve pairs of nerves that emerge directly from the brain, not through the spinal column, serving various sensory and motor functions of the head and neck.
Asymmetry
The lack of equality or equivalence between parts or aspects of something; not symmetrical.
Q7: The expressed (coding)regions of eukaryotic genes are
Q11: To determine the phenotype of an individual
Q19: STR analysis is a DNA profiling technique
Q30: The temperate zones _.<br>A) have the coolest
Q33: Some biologists urge the collection of the
Q34: Lysosomes are responsible for _.<br>A) lipid synthesis<br>B)
Q36: An individual heterozygous for cystic fibrosis _.<br>A)
Q41: Which of the following is not a
Q42: Some ribosomes are suspended in the cytosol
Q46: Proteins are polymers constructed from _ monomers.<br>A)